How to Write Masters Dissertation/ Thesis
admin2023-06-22T14:11:13+05:30How to Write a Dissertation /Thesis for Masters PhD

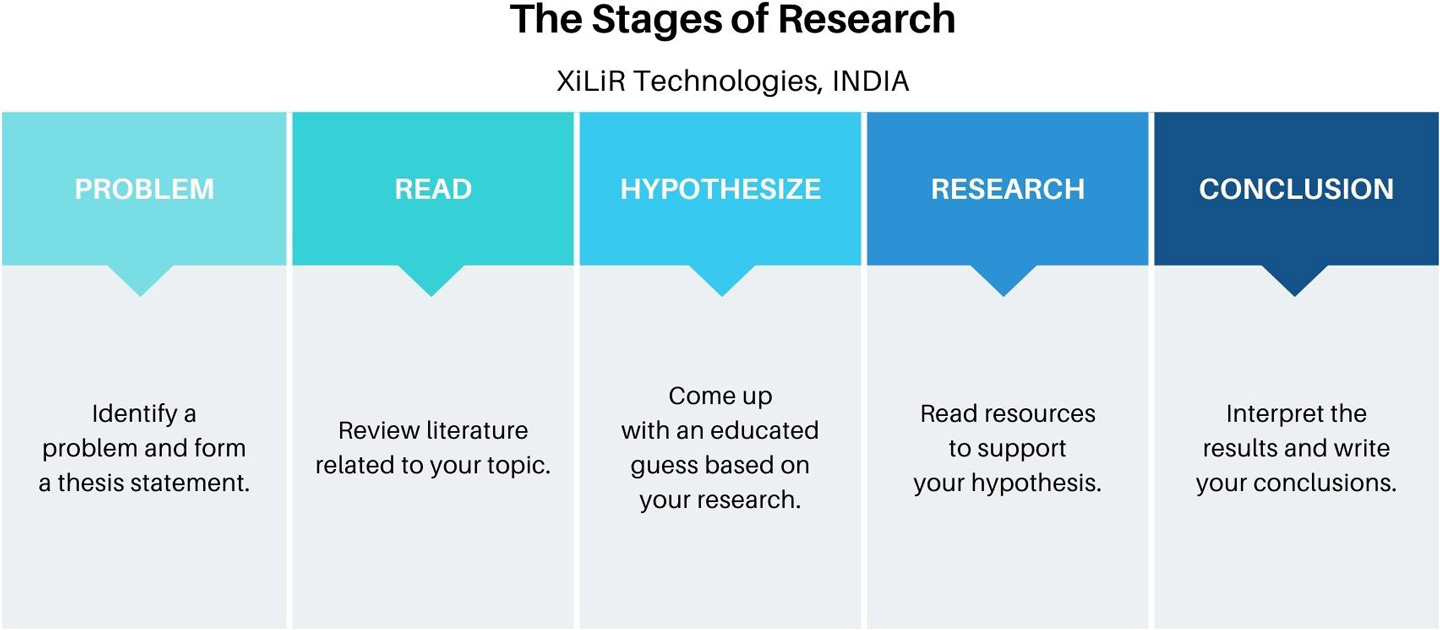
Whats is Dissertation ?
Different levels of academic mastery are shown in dissertations and theses.Master’s students in the U.S. usually write theses, while doctoral students usually write dissertations.
How to Write a Dissertation Thesis : Step-by-Step Guide
How to Write a Dissertation Thesis : Step-by-Step Guide
Content / Steps in Writing PhD Master Thesis
- Title page
- Deceleration
- Certificate
- Acknowledgments
- Abstract
- Table of Contents
- List of Figures and Tables
- List of Abbreviations
- Introduction (Chapter 1)
- Literature review (Chapter 2)
- Methodology (Chapter 3)
- Implementation & Results (Chapter 4)
- Conclusion (Chapter 5)
- Reference list
- Appendices
- Bibliographic
- List of Publications
You can Take Help from us for Completing your Masters Thesis Work !
OUR HIGHTLIGHTS
IEEE Latest Base Paper Proposed Work Training Viva Preparation Thesis - Plagfree : Turnitin Research Paper Writing Publication - IEEE, UGC, Scopus etc. Till Last Moment Support Direct Contact with Developer
Feel Free to Contact Us Now For Help
1. Title page/ Cover Page
2. Deceleration
3. Certificate
4. Acknowledgements
The acknowledgements section, which is typically optional, provides space for you to express gratitude to everyone who supported your dissertation’s creation.
This may include your mentors, study subjects, and close friends or family who helped you.
5. Abstract
- List the major focus and objectives of your study. Describe the research methodologies you employed.
- summarise the key findings
- Summarize your findings.
6. Table of Contents
7. List of Figures and Tables
8. List of Abbreviations
9. Introduction (Chapter 1)


Before you begin your research, you should have done a literature review to learn everything you can about the academic work that has already been done on your topic. In the literature review chapter or section of your dissertation, you shouldn’t just summarize the studies that have already been done. Instead, you should create a clear structure and argument that shows why your own research is important. Many students make the mistake of thinking that the literature review chapter is just a summary of what other researchers have said.
- You need to combine the research that has already been done, not just summarise it. In other words, you need to show how the different parts of the theory fit together and what researchers agree on and what they don’t.
- You need to point out a hole in the research that your research will fill.In other words, you have to describe the problem in order for your research topic to offer a solution.
- You need to look at the research that has already been done to help you design your own research.
11. Methodology (Chapter 3)

This chapter describes and justifies the data gathering method used. This chapter also outlines how you analyzed your data. Begin by describing the method you chose and why this method was the most appropriate. In doing so, you should cite reference literature about the method. Next, detail every step of the data gathering and analysis process. Although this section varies depending on method and analysis technique chosen, many of the following areas typically are addressed:
- The overall approach and type of research (e.g. qualitative, quantitative, experimental, ethnographic)
- Your methods of collecting data (e.g. interviews, surveys, archives)
- Details of where, when, and with whom the research took place
- Your methods of analyzing data (e.g. statistical analysis, discourse analysis)
- Tools and materials you used (e.g. computer programs, lab equipment)
A discussion of any obstacles you faced in conducting the research and how you overcame them, an evaluation or justification of your methods
12. Implemention & Results (Chapter 4)

Discussion (According to Format, Discussion can be included in this section or Separate Chapter )
In the discussion, you talk about what your results mean and how they relate to your research questions. Here, you should give a detailed explanation of the results, talking about whether or not they met your expectations and how well they fit into the framework you built in earlier chapters. If any of the results came as a surprise, explain why this might be the case. It’s a good idea to think about how your data could be interpreted in different ways and talk about any limitations that could have affected the results.
13. Conclusion (Chapter 5)
14. Reference list
15. Appendices
Bibliographic essay. Questionnaire and coding manual, if any. Raw data.
16. Bibliographic
Include all relevant sources examined, whether cited or not.
17. List of Publications

Our Highlights
IEEE Latest Base Paper Proposed Work Training Viva Preparation Thesis - Plagfree : Turnitin Research Paper Writing Publication - IEEE, UGC, Scopus etc. Till Last Moment Support Direct Contact with Developer
We are Providing Master thesis in the field of





For ECE, EEE, EE & IE Projects
- Embedded System – Arduino, Raspberry pi 3, AVR
- VLSI Designing – Tanner Tools Hspice
- MATLAB Image processing, MATLAB Simulink
- Power Electronics, Power System
- Internet of things, Cloud Computing
- Antenna Designing – ANSYS HFSS
- Robotics, Drones , Mechatronics
- SIGNAL PROCESSING & Quadcopter, etc.
For CSE and IT Engineering
- Network Simulator NS2, NS3
- Internet of things, Cloud Computing
- WSN,MANET, VANET, DATA Mining
- SIGNAL PROCESSING
- Embedded System, Robotics
- IOT, Arduino, Embedded System
- ML, AI, Data mining ,etc.
For Mechanical Engineering
- Robotics, Mechatronics, Pneumatic based
- Hydraulic, Solar energy, Quadcopter, Drones
- Wind Energy Mechanical Engineering Design
- Industrial and Production Engineering
- Automobile Engineering
- Computer-Aided Engineering Mechatronics Engineering
- Power Plant Engineering, etc.
For Civil Engineering
- Environmental Engineering
- Geoinformatics
- Geothechnical Engineering
- Hydraulics and Water Resources Engineering
- Infrastructure Engineering and Management
- Structural Engineering
- Transportation Engineering, etc.